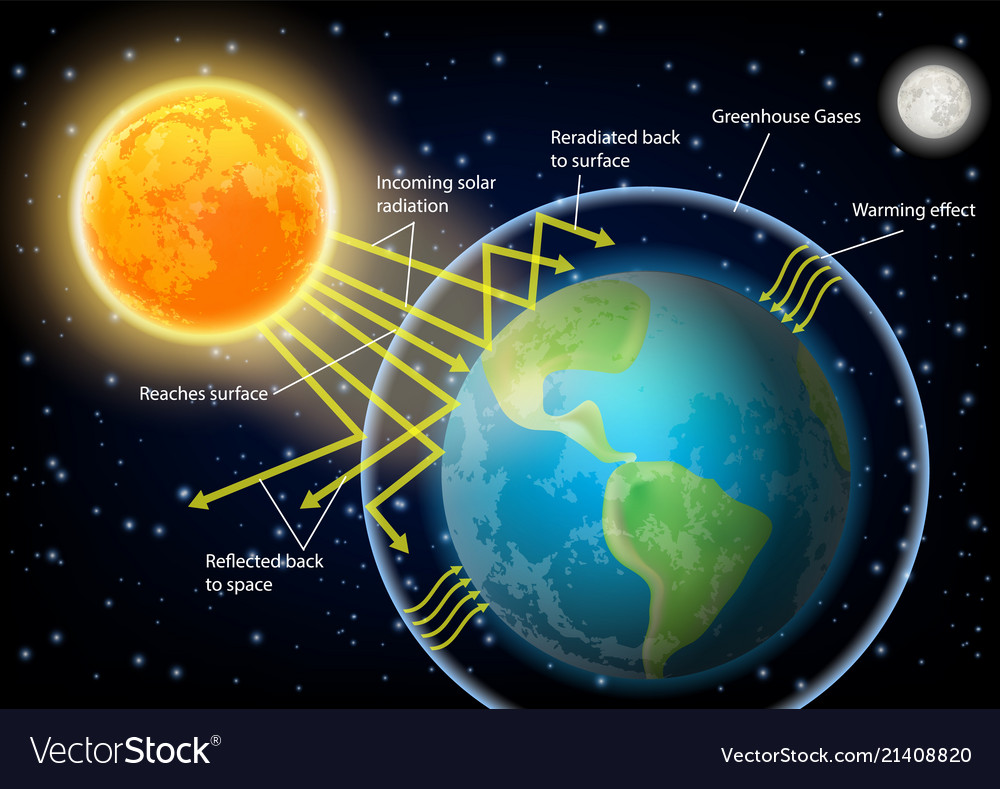
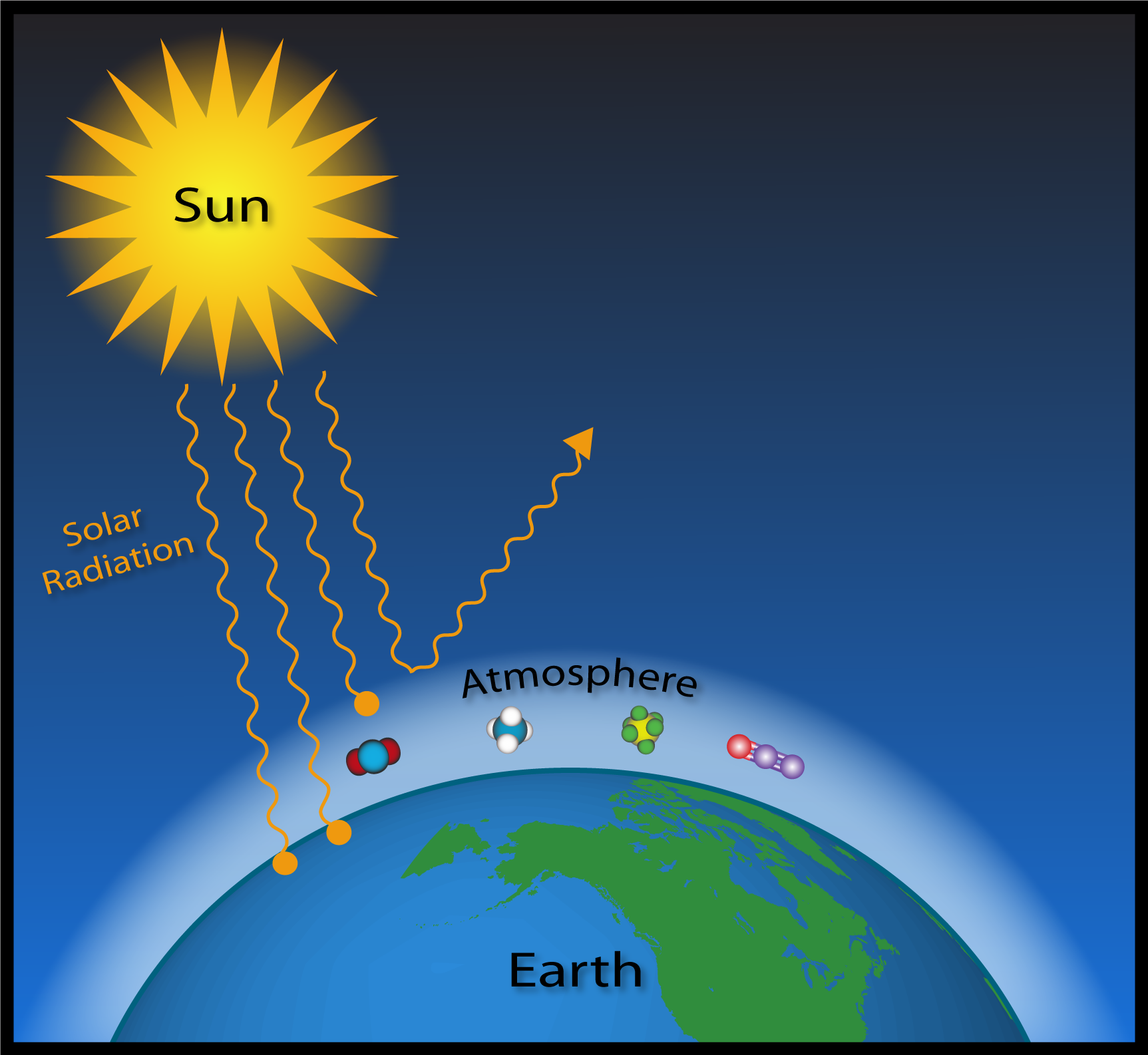
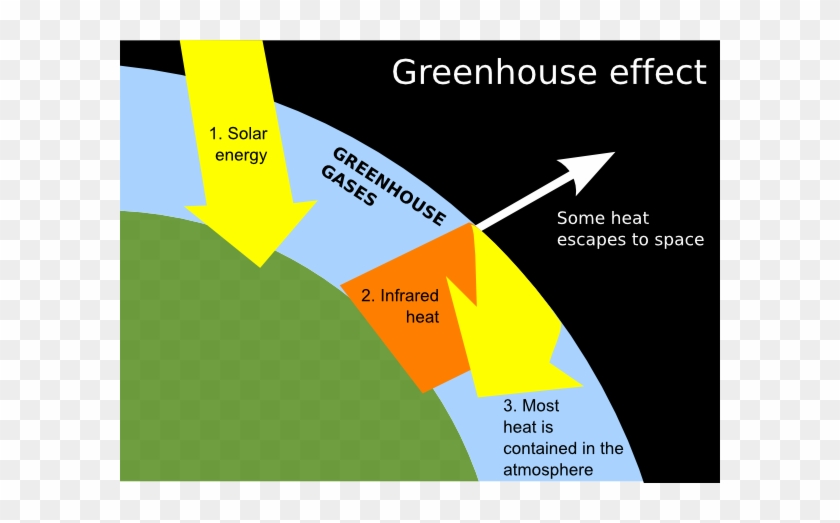
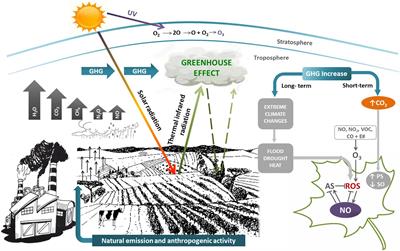
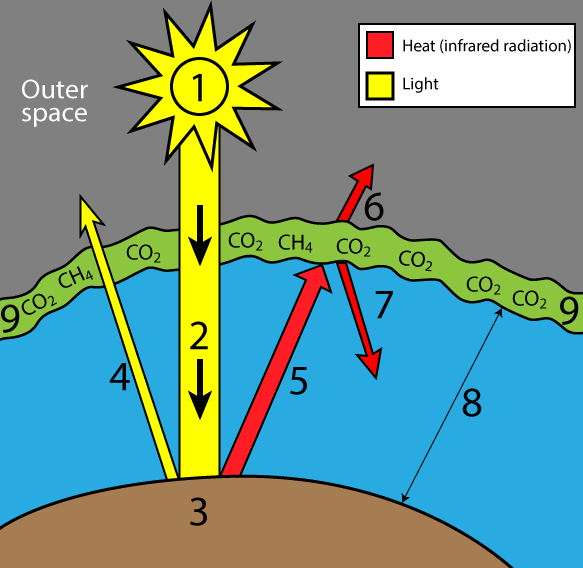
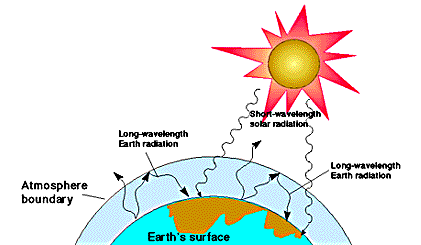
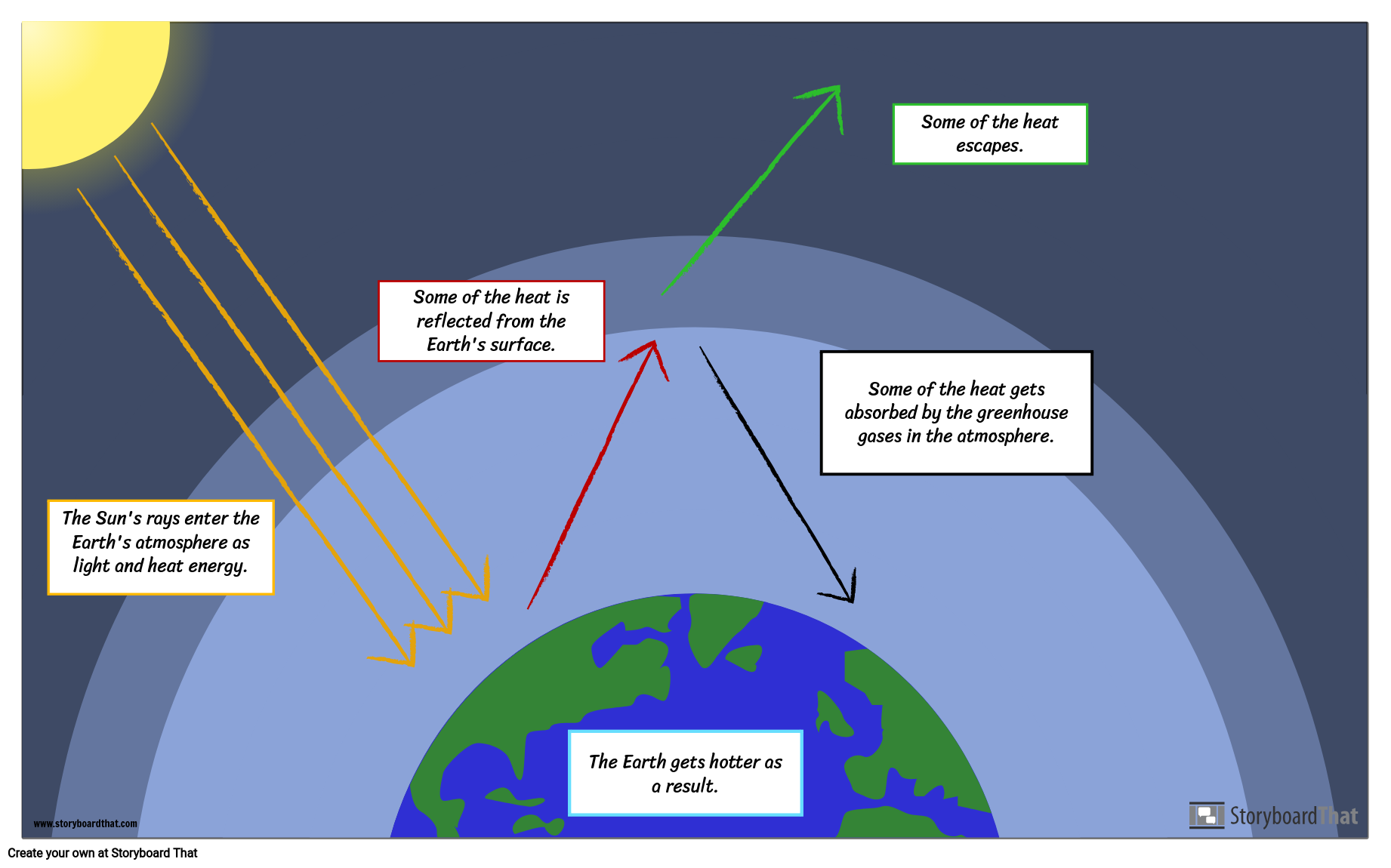
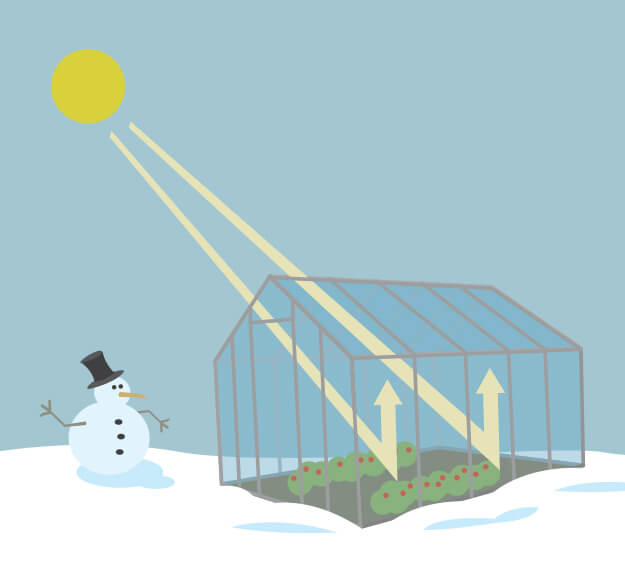
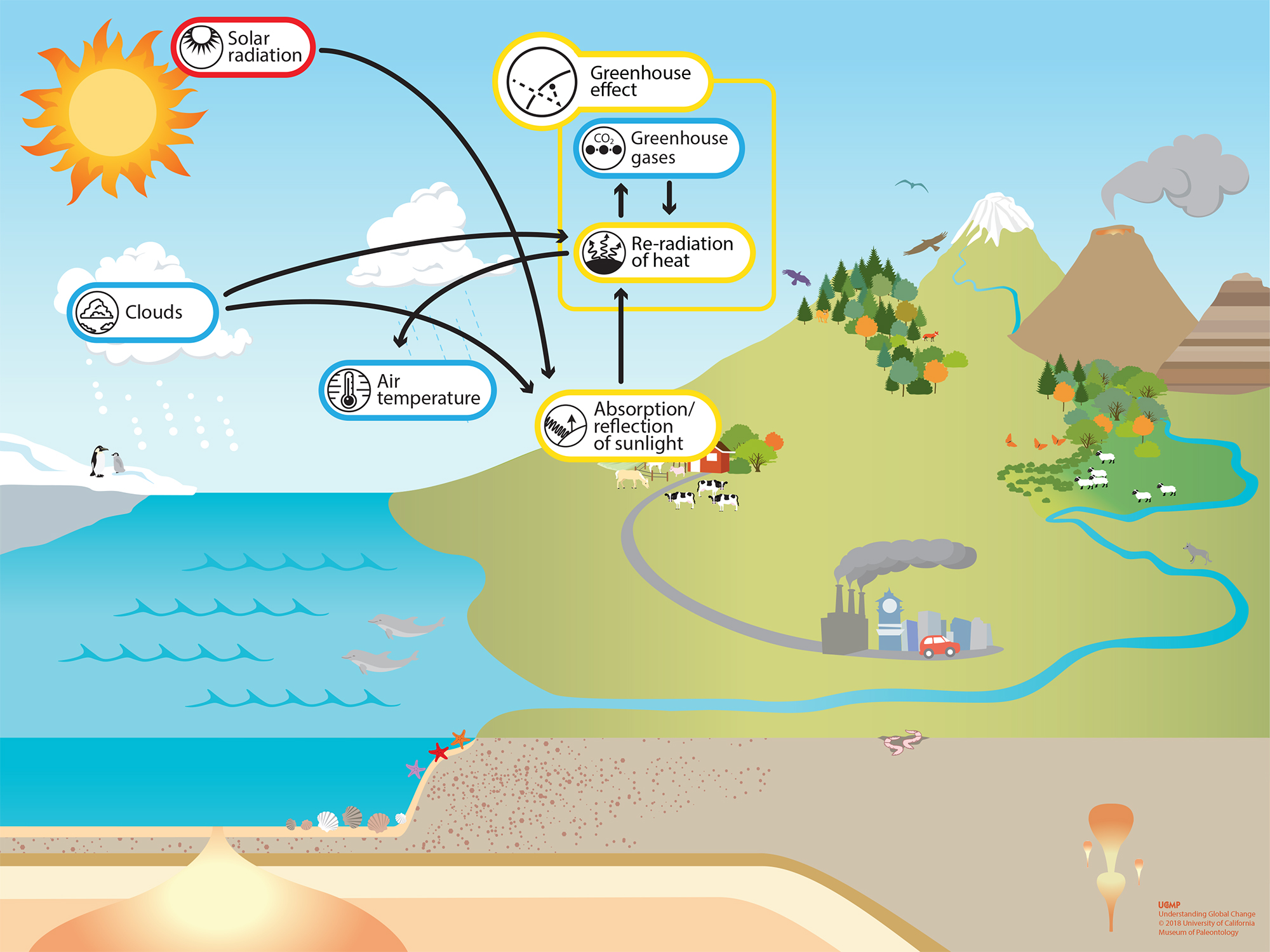
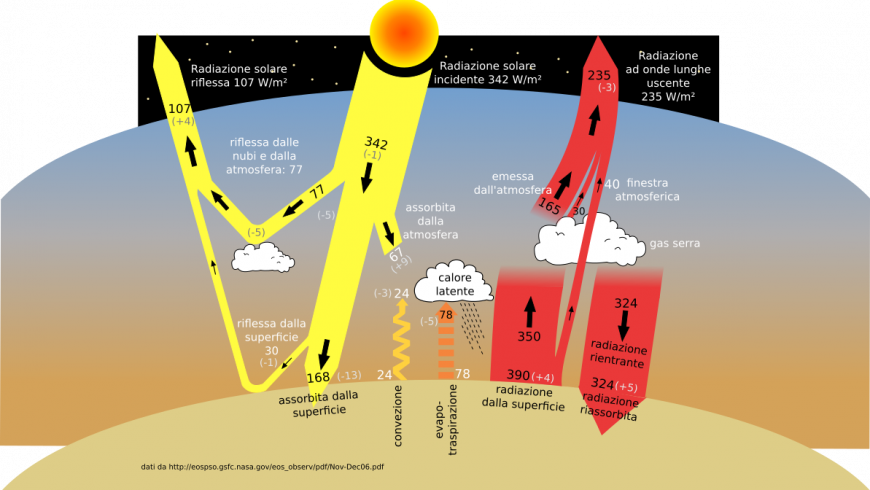
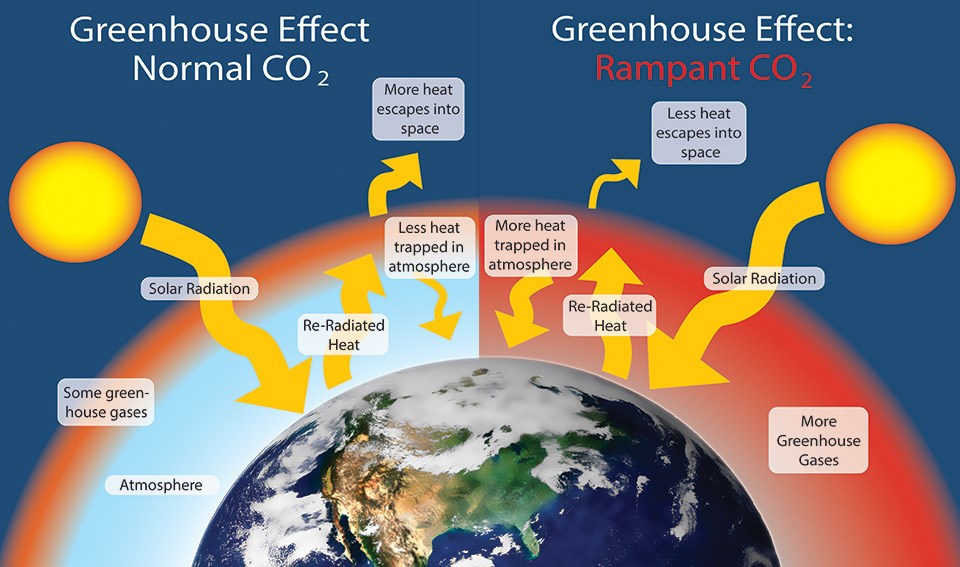
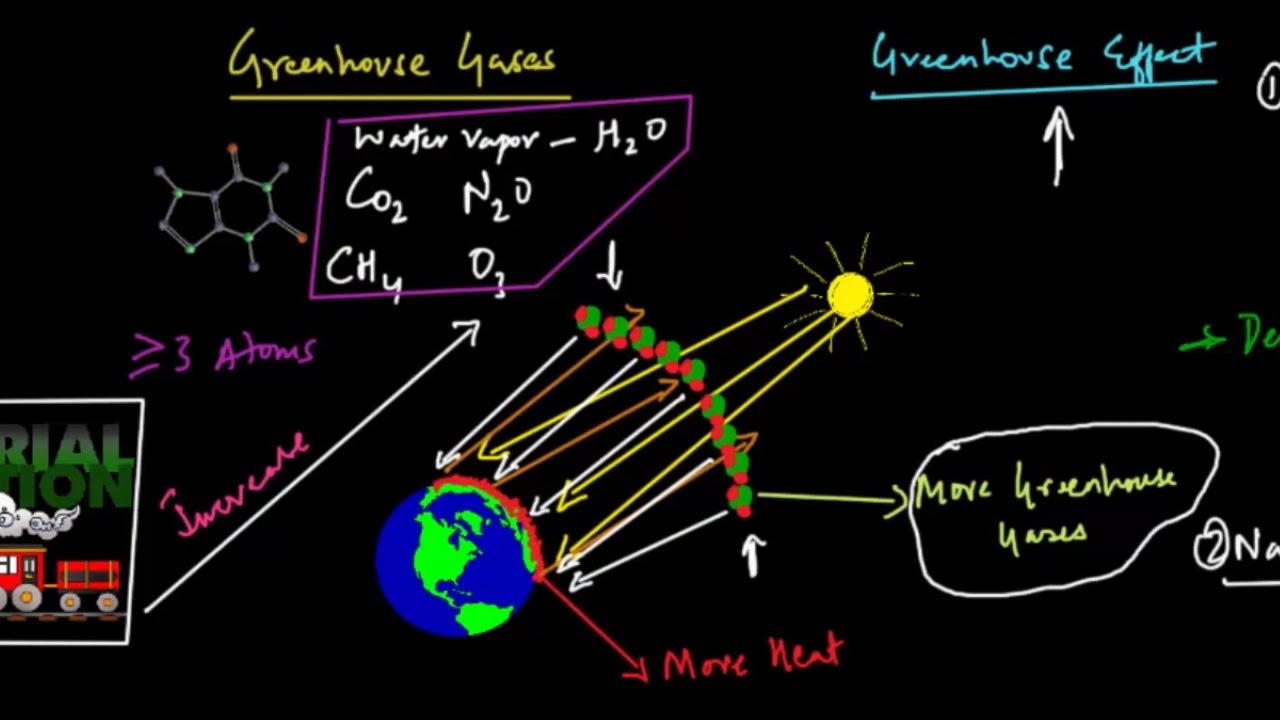
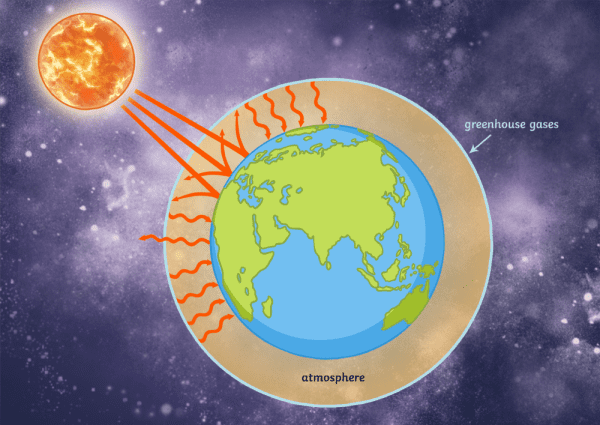
The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect
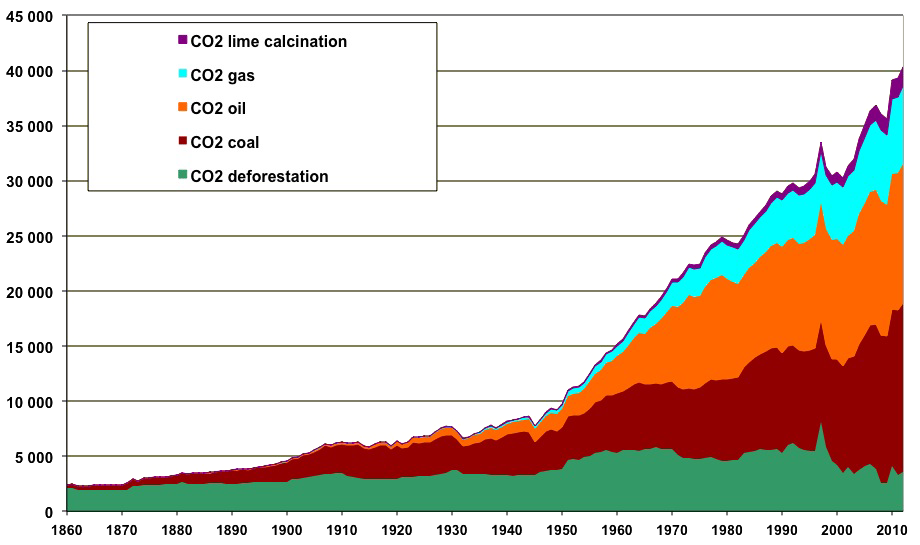
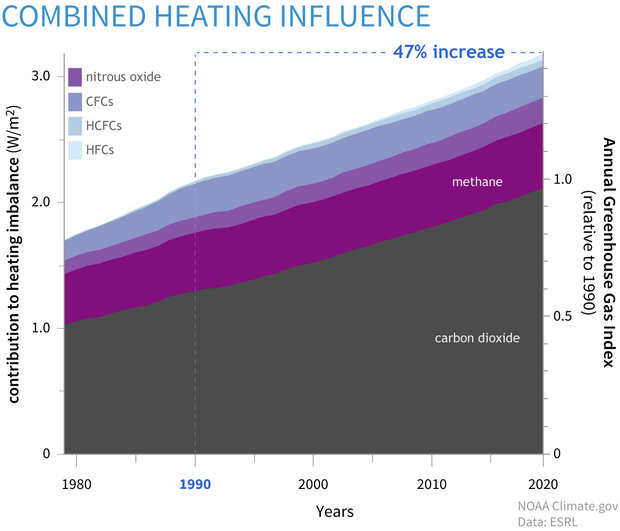
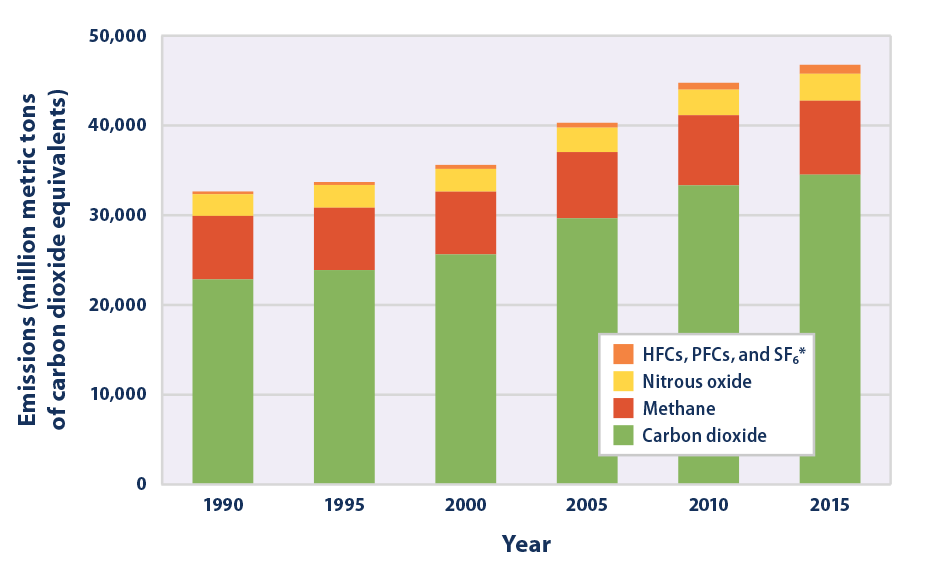
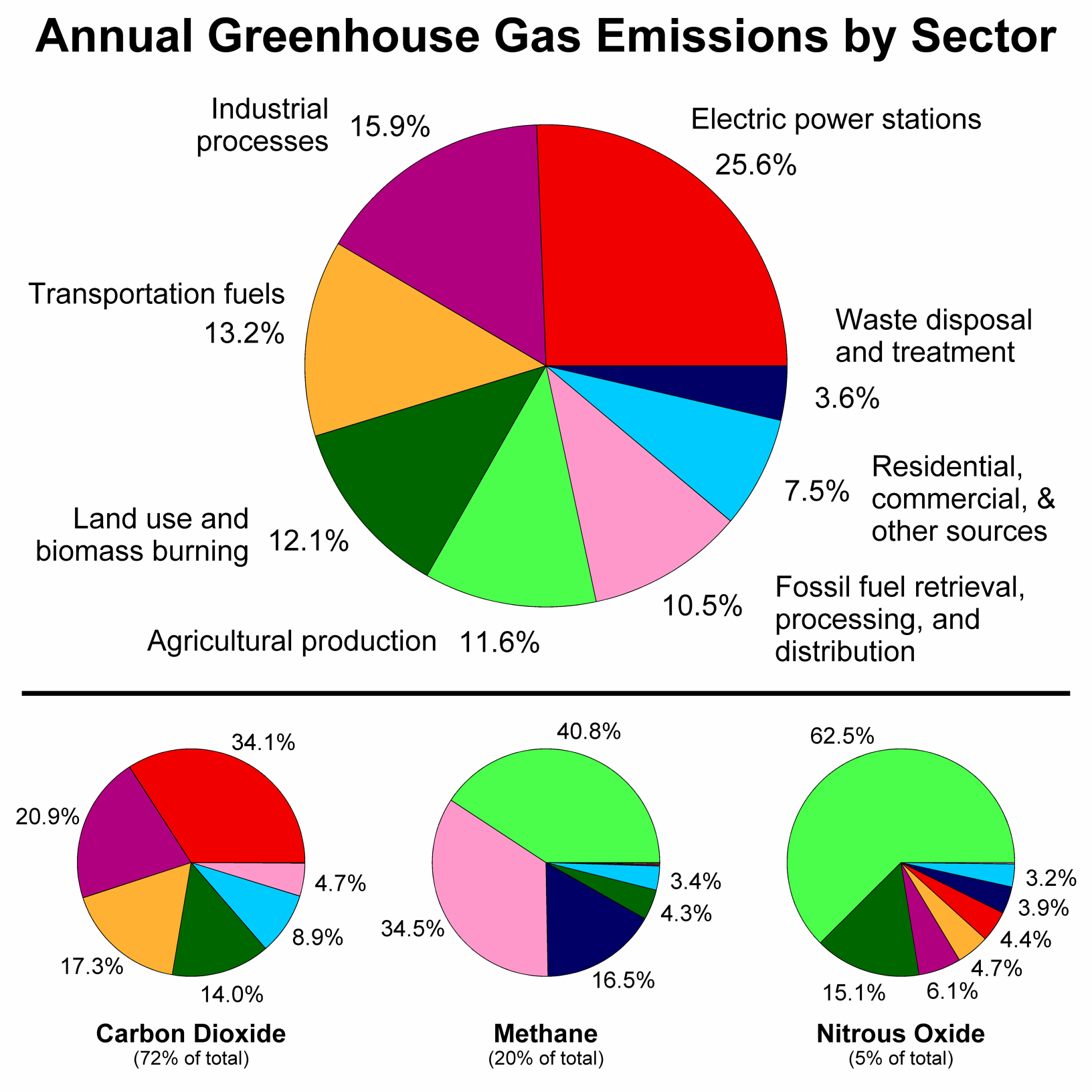
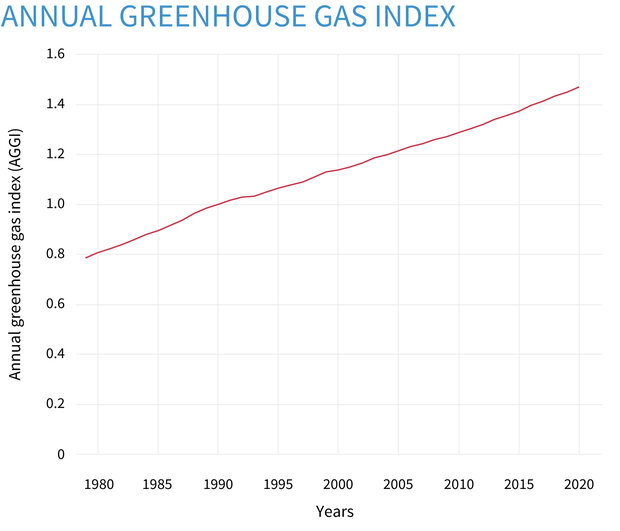
Greenhouse gas diagram of the greenhouse effect-In terms of the net increase in the greenhouse effect due to humanproduced greenhouse gases, CO 2 is responsible for the lion's share CO 2 from fossil fuel burning alone is more than half the net force If you add CO 2 from fossil fuel burning, deforestation, and other minor sources, this comes to a little more than threefourths of the netGreenhouse Effect Contents Atmosphere Key Terms Gases Causes Effects Atmosphere Exosphere Thermosphere Mesosphere Stratosphere Troposphere Troposphere Lowest portion of earth's atmosphere 75% of the entire atmosphere mass Water Vapor Aerosols 0 km – 10 km Depth ~ 10 km Warmer nearest earth Colder the further you go Travel Back to the Atmosphere Stratosphere
Greenhouse gas diagram of the greenhouse effectのギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「Greenhouse gas diagram of the greenhouse effect」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 | ||
 |  |  |
 | .png) |  |
「Greenhouse gas diagram of the greenhouse effect」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 | ||
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/greenhouse-effect-vector-diagram-889624280-6670a804e4d2472eb71892d746c8d0df.jpg) |  |
「Greenhouse gas diagram of the greenhouse effect」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 | ||
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「Greenhouse gas diagram of the greenhouse effect」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「Greenhouse gas diagram of the greenhouse effect」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「Greenhouse gas diagram of the greenhouse effect」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「Greenhouse gas diagram of the greenhouse effect」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「Greenhouse gas diagram of the greenhouse effect」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
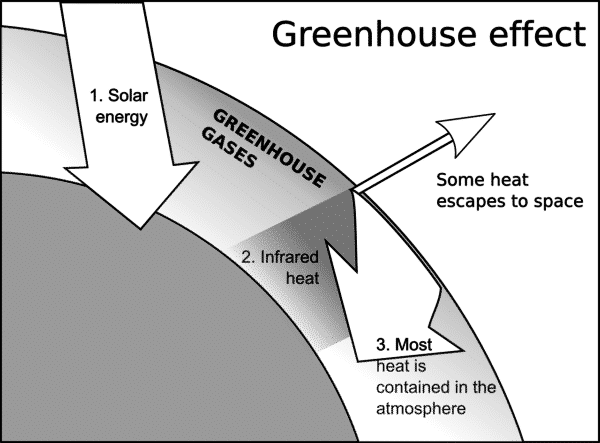 |  |
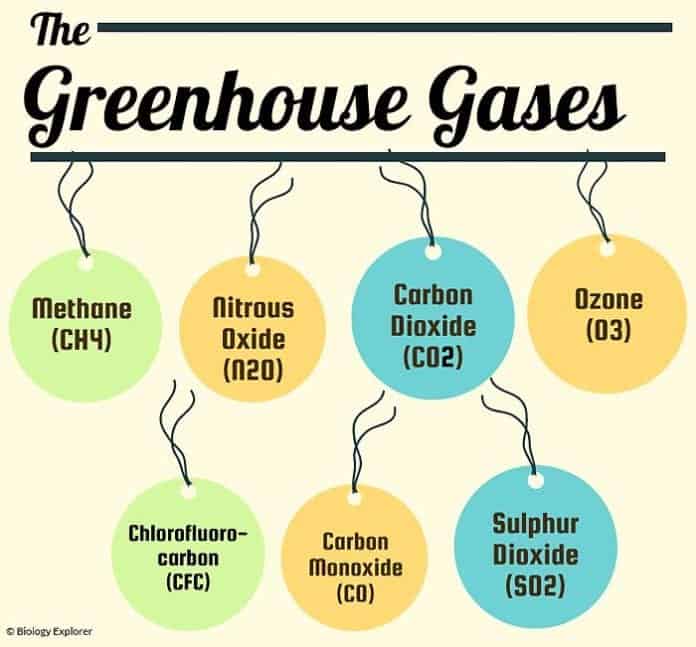
Five Major Greenhouse Gases The most significant gases that cause global warming via the greenhouse effect are the following Carbon Dioxide Accounting for about 76 percent of global humancausedThe greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directions Part of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming it Similarly, aerosols have radiatively active effects





0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿